Atoms: The Basic Building Blocks
Imagine everything around you, from the chair you're sitting on to the air you breathe, being built from tiny, indivisible particles. These are atoms, the basic unit of matter. Just like Legos come in different shapes and sizes, there are over 100 different types of atoms, each with a unique identity.
Protons atom
Protons atom are subatomic particles with a positive electric charge. They are one of the three main components of an atom, along with neutrons and electrons. Protons atom are located in the nucleus of an atom, which is the central core of the atom. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus determines the element's atomic number. For example, all hydrogen atoms have one proton in their nucleus, all helium atoms have two protons in their nucleus, and so on.
Here are some of the key properties of protons:
Charge
Protons atom have a positive electric charge of +1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs. This positive charge is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the negative charge of an electron.
Mass
Protons atom have a mass of approximately 1.6726 x 10^-27 kilograms. This mass is about 1,836 times the mass of an electron.
Size
Protons atom are very small particles. Their diameter is about 1.6 femtometers (fm). A femtometer is equal to 10^-15 meters.
Structure
Protons atom are thought to be made up of even smaller particles called quarks. Quarks are fundamental particles that are not made up of any other subatomic particles. Protons are made up of two up quarks and one down quark.
The number of protons atom in an atom's nucleus is very important. It determines the element's identity. An element is a substance that is made up of atoms that all have the same number of protons in their nuclei. For example, all atoms of the element hydrogen have one proton in their nucleus, all atoms of the element helium have two protons in their nucleus, and so on. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is also known as the atomic number of the element. The atomic number is a unique identifier for each element.
Neutrons atom: The Unsung Heroes of the Nucleus
Neutrons atom, alongside protons, reside in the heart of an atom – the nucleus. Often overshadowed by their positively charged counterparts, neutrons play a crucial role in defining an atom's stability and identity.
Properties of Neutrons:
Charge
Unlike protons atom, neutrons atom are electrically neutral. They carry no charge (neither positive nor negative). This unique property allows them to act as a mediator between positively charged protons within the nucleus.
Mass
Neutrons atom are surprisingly hefty subatomic particles. Their mass is nearly identical to that of a proton, clocking in at around 1.6749 x 10^-27 kg. This significant mass contributes to the overall mass of an atom, which is crucial for understanding various chemical reactions.
Size
Similar to protons atom, neutrons atom are incredibly small. Their diameter is approximately 1.6 femtometers (fm), which is an unimaginably tiny unit (10^-15 meters).
Structure
Unlike protons, which are composed of quarks, the exact structure of neutrons is a topic of ongoing research. However, the current understanding suggests they are made up of even smaller fundamental particles called up and down quarks, but in a different combination than protons (one up quark and two down quarks).
Role of Neutrons atom in the Nucleus
Stability: The strong nuclear force, a powerful attractive force, binds protons and neutrons together within the nucleus. Neutrons, lacking electrical repulsion, help to stabilize the nucleus, especially in isotopes with more protons.
Isotopes: Atoms of the same element can have varying numbers of neutrons, giving rise to isotopes. These isotopes have the same atomic number (number of protons) but different atomic masses due to the varying number of neutrons. For example, Carbon-12 (6 protons and 6 neutrons) and Carbon-14 (6 protons and 8 neutrons) are isotopes of carbon. The presence of neutrons can influence the stability of isotopes, with some isotopes being radioactive due to an unstable nucleus.
Electrons atom: Tiny Dancers in the Atomic Scheme
Electrons atom are the fundamental building blocks of the electron cloud surrounding an atom's nucleus. Understanding their properties and behavior is crucial in MBBS for grasping concepts in biochemistry, biophysics, and even drug interactions.
Properties of Electrons:
Charge
Electrons atom possess a negative electric charge of -1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs. This negative charge is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the positive charge of a proton. The attraction between oppositely charged electrons and protons holds the atom together.
Mass
Electrons atom are incredibly light compared to protons and neutrons. Their mass is approximately 9.109 x 10^-31 kg, which is about 1/1836th the mass of a proton.
Size
Electrons atom are even smaller than protons. Their size is difficult to define precisely due to their wave-particle duality, but it's estimated to be on the order of a point charge with no measurable diameter.
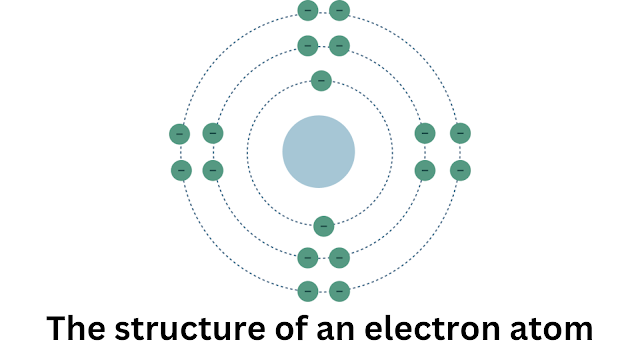
Energy Levels and Orbitals: Electrons atom don't exist in fixed positions within the atom. Instead, they occupy specific energy levels or orbitals. These orbitals define the probability of finding an electron in a particular region around the nucleus.
Electron Configuration and Chemical Behavior:
The arrangement of electrons in orbitals determines an atom's chemical behavior. Electrons in the outermost energy level, called the valence shell, are most crucial for forming chemical bonds with other atoms.
Understanding electron configuration allows you to predict the types of bonds (ionic, coval
ent) an atom can form and its overall reactivity.
People also asked
Q.1 What is a proton atom?
Ans.
Protons: Protons atom are subatomic particles, not whole atoms. They reside within the nucleus of an atom, along with neutrons. Protons have a positive electric charge.
Q.2 What is the atomic mass of a proton?
Ans. Proton atom mass (amu) ≈ 1.0072766 amu
Proton mass (kg) ≈ 1.6726 x 10^-27 kg.
Q.3 What is neutron and proton?
Ans. Protons atom: positively charged (+), massive building blocks, define element identity.
Neutrons: no charge (neutral), massive building blocks, help stabilize nucleus.
Q.4 What is the electric charge of a Neutron.
Ans. The electric charge of a neutron atom is zero. Neutrons are neutral particles, meaning they don't carry any electric charge – neither positive nor negative. This unique property allows them to act as a mediator between the positively charged protons within the nucleus.
Q.5 what is electron atom change?
Ans. Electrons atom are like tiny dancers in the atom, constantly moving around the nucleus. But their moves aren't random! They occupy specific energy levels, influenced by the pull of the nucleus. Here's the gist of electron changes:
Energy Jumps: Imagine the electron dancers leaping between different levels. They can absorb energy (like a boost) to jump to a higher level (excited state). This extra energy is often released later as light.
Losing the Groove: If an electron absorbs enough energy, it can completely escape the atom's grip, becoming unbound (ionization). This creates a charged ion, important in chemical reactions.
Bonding Moves: Electrons in the outermost level (like the lead dancers) are key players in forming chemical bonds. They can be shared (covalent bonding) or transferred (ionic bonding) between atoms, leading to the formation of molecules. This electron dance is crucial for understanding how chemicals interact in our bodies (biochemistry) and how drugs work.




0 Comments
if you have any doubts please let me now